Path Planning Algorithms
Path Planning Algorithms
Section titled “Path Planning Algorithms”Comprehensive path planning implementation featuring Bi-Directional Rapidly-exploring Random Trees (Bi-RRT) and Artificial Potential Field (APF) methods for robot navigation in complex environments.
Path Planning Visualizations
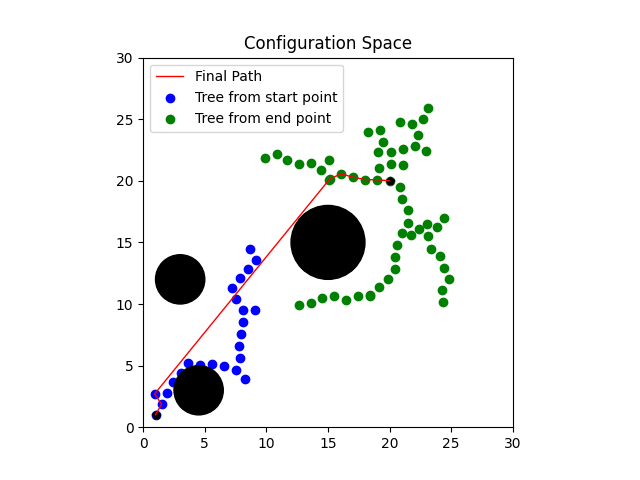
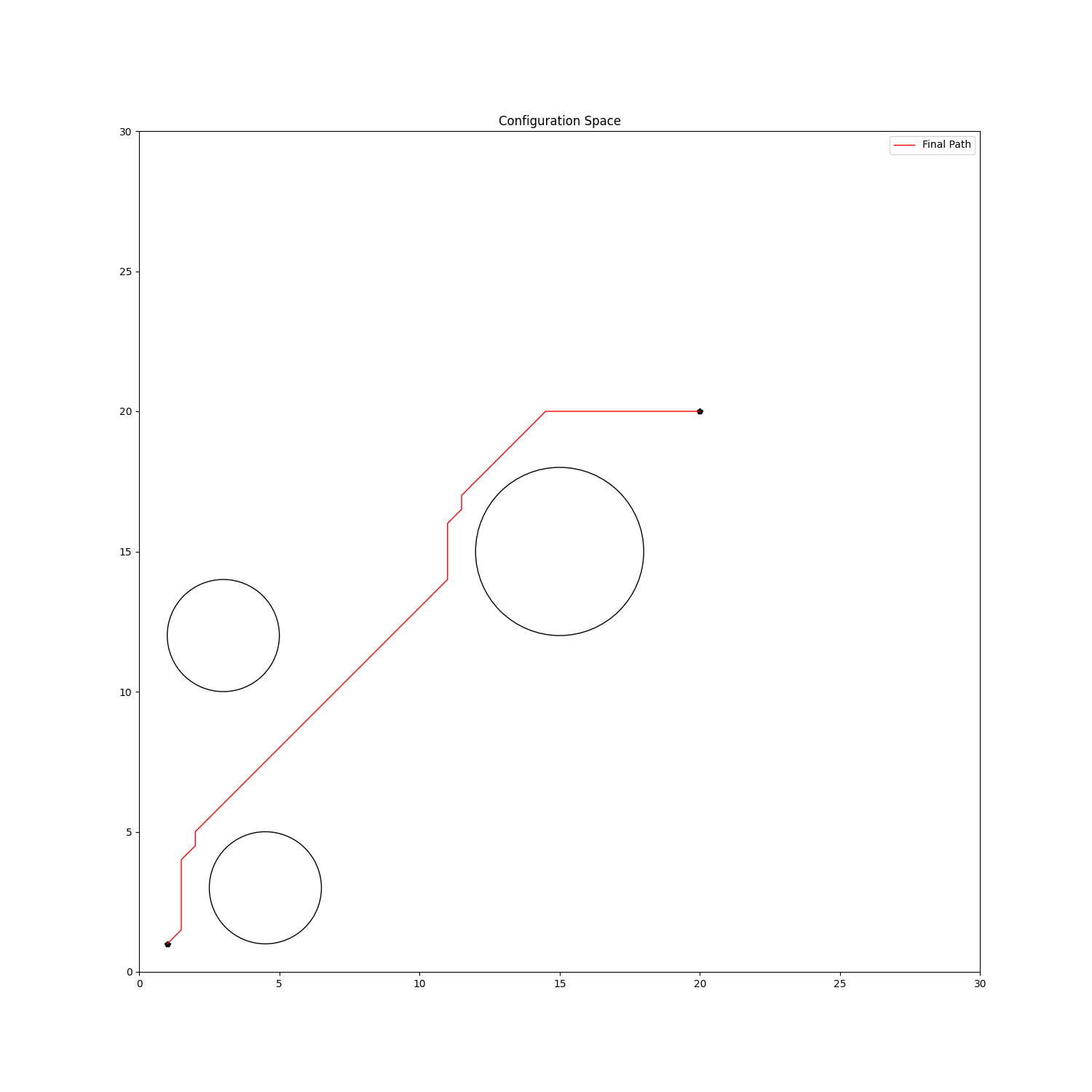
Algorithm Overview
Section titled “Algorithm Overview”Path planning is fundamental to robotics and autonomous systems, determining optimal collision-free paths from start to goal positions while respecting environmental constraints and kinematic limitations.
Bi-Directional RRT
Section titled “Bi-Directional RRT”An efficient sampling-based algorithm that grows two trees simultaneously from start and goal positions, significantly improving convergence speed over traditional single-tree RRT.
Algorithm Principles
Section titled “Algorithm Principles”Bi-RRT operates on the principle of dual exploration:
- Simultaneous Tree Growth: Two trees expand from start and goal positions
- Random Sampling: Generates random configurations in configuration space
- Tree Connection: Attempts to connect trees when they approach each other
- Path Extraction: Once connected, extracts complete path
Mathematical Foundation
Section titled “Mathematical Foundation”The algorithm explores configuration space C using random sampling:
Tree expansion follows:
Where is the step size parameter.
Implementation Details
Section titled “Implementation Details”# Bi-RRT execution with custom iterationspython bi_rrt.py --iter 200
# Default configuration (100 iterations)python bi_rrt.pyArtificial Potential Fields
Section titled “Artificial Potential Fields”A physics-inspired approach that models the environment as potential fields, where obstacles generate repulsive forces and the goal generates attractive forces.
Potential Field Theory
Section titled “Potential Field Theory”The total potential at any point q is the superposition:
Where:
- is the attractive potential from the goal
- is the repulsive potential from obstacle i
Attractive Potential Functions
Section titled “Attractive Potential Functions”Two formulations are supported:
Parabolic Function:
Conical Function:
Repulsive Potential
Section titled “Repulsive Potential”For obstacle i with distance :
Where is the influence distance and is the repulsive gain.
Implementation
Section titled “Implementation”# Custom configurationpython pf.py --grid 0.5 --function conical --attractive 1 --repulsive 5000
# Default settingspython pf.pyStreamlit Visualization
Section titled “Streamlit Visualization”Interactive web-based visualization using Streamlit for real-time algorithm demonstration and parameter tuning.
Features
Section titled “Features”- Real-time Visualization: Watch algorithms explore the space
- Parameter Adjustment: Modify algorithm parameters during execution
- Multiple Algorithms: Switch between Bi-RRT and APF methods
- Environment Customization: Define custom obstacle configurations
- Path Analysis: Examine generated paths and algorithm performance
Launch Interface
Section titled “Launch Interface”streamlit run app.pyAlgorithm Comparison
Section titled “Algorithm Comparison”Different path planning approaches offer distinct advantages for various scenarios.
Bi-RRT Characteristics
Section titled “Bi-RRT Characteristics”Advantages:
- Probabilistic Completeness: Guaranteed to find a path if one exists
- High-Dimensional Support: Works well in complex configuration spaces
- Fast Convergence: Bidirectional search improves efficiency
- Optimality: Can approach optimal solutions with sufficient iterations
Limitations:
- Non-Deterministic: Path quality varies between runs
- Parameter Sensitivity: Performance depends on step size and iterations
- Memory Usage: Tree structures can grow large
APF Characteristics
Section titled “APF Characteristics”Advantages:
- Deterministic: Reproducible paths for given configurations
- Real-time Capability: Suitable for dynamic environments
- Smooth Paths: Naturally generates smooth trajectories
- Local Optimality: Converges to local minima
Limitations:
- Local Minima: Can get trapped in non-optimal solutions
- Narrow Passage Difficulty: Struggles with tight corridors
- Parameter Tuning: Requires careful gain selection
- Completeness Issues: Not guaranteed to find paths
Applications
Section titled “Applications”- Mobile Robotics: Autonomous navigation in unknown environments
- Manipulator Planning: Robot arm trajectory planning
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving car path planning
- Game AI: Non-player character navigation
- Aerospace: Aircraft trajectory optimization
Technical Requirements
Section titled “Technical Requirements”pip install -r requirements.txtDependencies include NumPy for numerical computations, Matplotlib for visualization, and Streamlit for the interactive interface.
Implementation Notes
Section titled “Implementation Notes”The modular design allows easy extension with additional algorithms and supports both 2D and 3D planning spaces with minimal modification.